John Errington's tutorial on Power Supply Design
Load regulation of smoothed full wave rectified supply
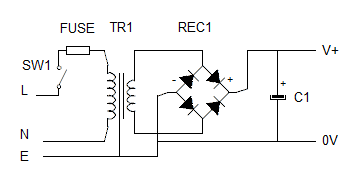 When we increase the load on this type of supply the output voltage drops.
When we increase the load on this type of supply the output voltage drops.
The load regulation is
load regulation = (Voc - Vrated) / Vrated
where Voc = open circuit voltage and
Vrated = output voltage at full rated load
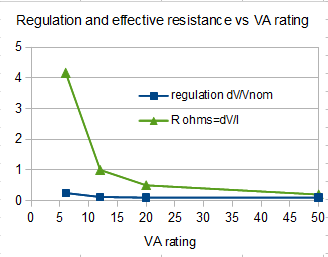
Typical regulation factor for small mains transformers are as follows:
| VA rating | Regulation | Reff ohms |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.25 | 4 |
| 12 | 0.12 | 1 |
| 20 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| 50 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 100 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
For a resistive load and sinusoidal waveform the regulation is due to copper losses - resistance in the transformer windings. In power supplies the load is not purely resistive and the waveform is not purely sinusoidal. These factors make accurate calculation of the expected regulation virtually impossible.
(The situation is even worse for half wave rectification.)
For our purposes we can assume the transformer behaves as an ideal sinusoidal voltage source with a series resistance at the secondary.
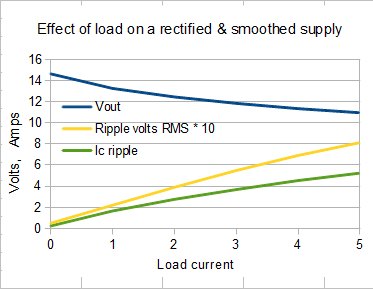
This chart shows the behaviour of output voltage, ripple voltage and ripple current in capacitor with increasing loads.
The components used are as follows:
Tr1 Vpk = 17.0V
VfRec = 2.0V
Rint TR1 = 0.5 ohm
F = 100Hz (2*50Hz)
C1 = 10mF (10,000uF)
If we take 2A as the rated output current the load regulation for this supply would be
%Vlreg= 100*13.6-12.5/12.5 = 8.8%
Conclusion
When designing a simple linear rectified and smoothed power supply as shown in the figure above the output at full load will be Vrms(full load) = 1.4*Vrms(nominal) - Vf(rectifier) - Vpk-pk(ripple)/2
Example:
For a 12v 2A supply using a 12V transformer and 4700uF capacitor
Vpk-pk(ripple) = Iload / fC = 2/100*0.0047 = 4.25V
Vrms(full load) = (1.4 * 12V = 16.8V) - 2V - 2.1V = 11.9V
PSUDesigner is a freeware simulator package you can use to check your design.